Prerequisites for 7-hour large scale production
In this scenario, very specific types of hardware and software are utilized to enact such a large scale virtual machine (VM) and pod deployment. Keep in mind that your organization’s needs may vary, but the applications of the software described can overlap in similar situations.
What will you learn?
- Specific hardware and software components used during this scenario
What do you need before starting?
Software prerequisites
As part of this exercise, the steps provided will include fine-tuning Red Hat® Ceph® Storage and Red Hat OpenShift® Virtualization. The following software components are necessary for this:
- Red Hat OpenShift (version 4.13.2 or higher)
- Red Hat Ceph Storage (version 5.3.2 or higher)
- Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation (version 4.12.3 or higher)
- Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization (version 4.13 or higher)
Hardware prerequisites
This deployment scenario utilizes specific hardware for Openshift Container Platform and Red Hat Ceph storage.
OpenShift Container Platform hardware
- 132 PowerEdge R650
- CPU: 112 cores (2 Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6330N CPU @ 2.20GHz)
- Memory: 512 GB (16 Micron MTA36ASF4G72PZ-3G2E7 32GB Ddr4 3200Mhz PC4-25600 Ecc)
- SSD (root disk): 446.63 GB - 6 Gbps (MICRON SSD MTFDDAK480TDT)
- NVME: 3.2 TB (Dell Ent NVMe P5600 MU U.2
Red Hat Ceph Storage hardware
- 12 * Dell PowerEdge R750
- CPU: 40 cores (2* Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6230 CPU @ 2.10GHz)
- Memory: 384GB ECC RAM (12 * Samsung M393A4K40BB2-CTD 2666 MT/s)
- SSD Root disk: 1.92 TB (1 * SEAGATE XS1920LE70134)
- SSD Disk: 1862GiB - 6 Gbps (20 * SEAGATE XS1920LE70134)
- NVME disk: 1.8T - 3200 MB/s (4 * Dell Ent NVMe v2 AGN MU U.2 1.6TB)
With these software and hardware components in mind, we will explore a brief overview of the networking architecture for the Ceph and OpenShift clusters. In this example, the clusters are on a private lab VLAN uses the balance-alb bond using 4* 25 GbE ports creating a single 100GbE bond.
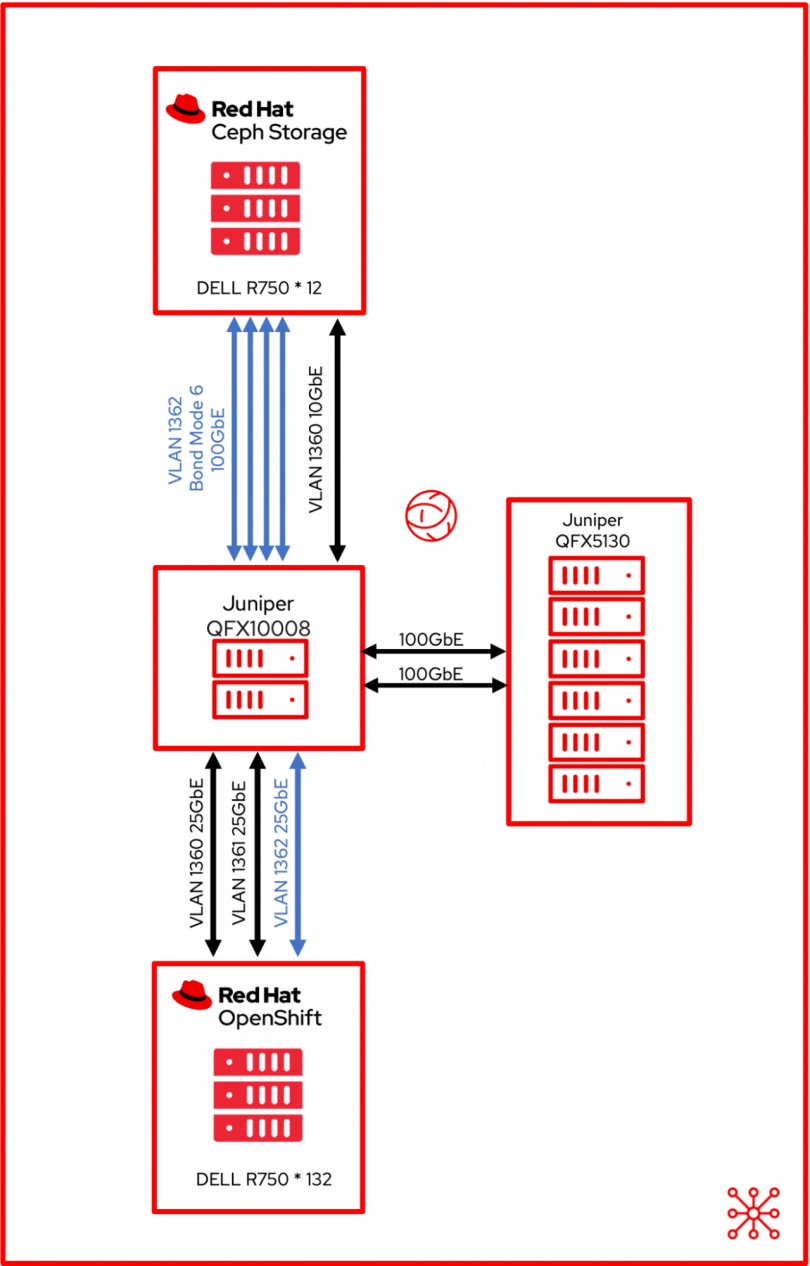
Now that the baseline needs are met, we’re ready to dive into this seven-hour journey to mass scaling of virtual machines.
