Using iSCSI storage for VMs on Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization in ROSA
With Red Hat® OpenShift® Virtualization you can run Virtual Machines (VMs) alongside containerized applications on the same Red Hat OpenShift cluster, managing both from a single platform. The ontap-san driver supports the RWX access mode in Block Volume Mode for iSCSI, making it ideal for VM disks and enabling live migration of VMs.
What will you learn?
- How to install Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
- How to deploy and customize VMs using iSCSI storage class
What you need before starting:
- Red Hat account
- Access to Red Hat OpenShift on the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console
- Amazon Web Services account
- IAM user credential with appropriate permissions to create and access ROSA cluster
- AWS command line-interface
- ROSA command line-interface
- OpenShift command-line interface (oc)
- Helm 3 documentation
- A HCP ROSA cluster
Verify you have baremetal nodes as worker nodes in the cluster.
To be able to create VMs, you need to have bare metal nodes on the ROSA cluster.
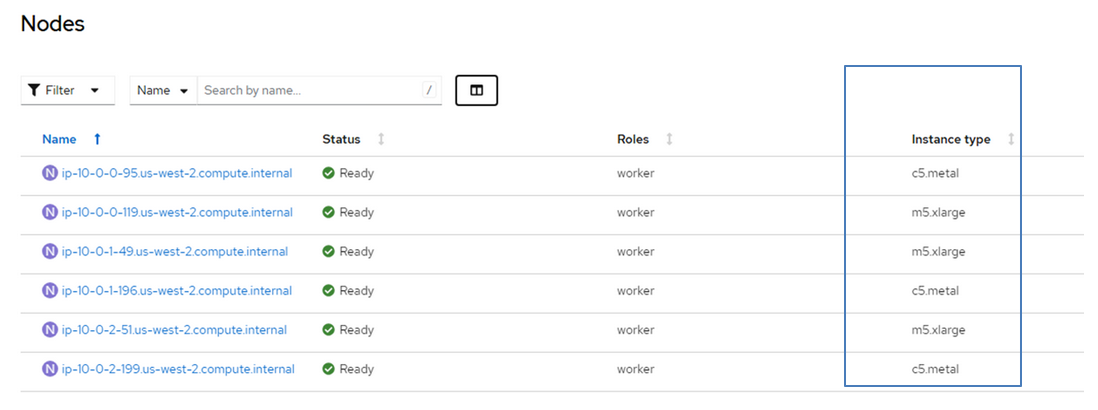
Figure 1: In the ROSA console under "Nodes" you can see that the c5.metal nodes are being used as the worker nodes.
Install Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization using the Operator
You can install Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization using the OpenShift Virtualization Operator in the Operator hub. Once it is installed and configured, Virtualization will be populated in the UI of the OpenShift Console.
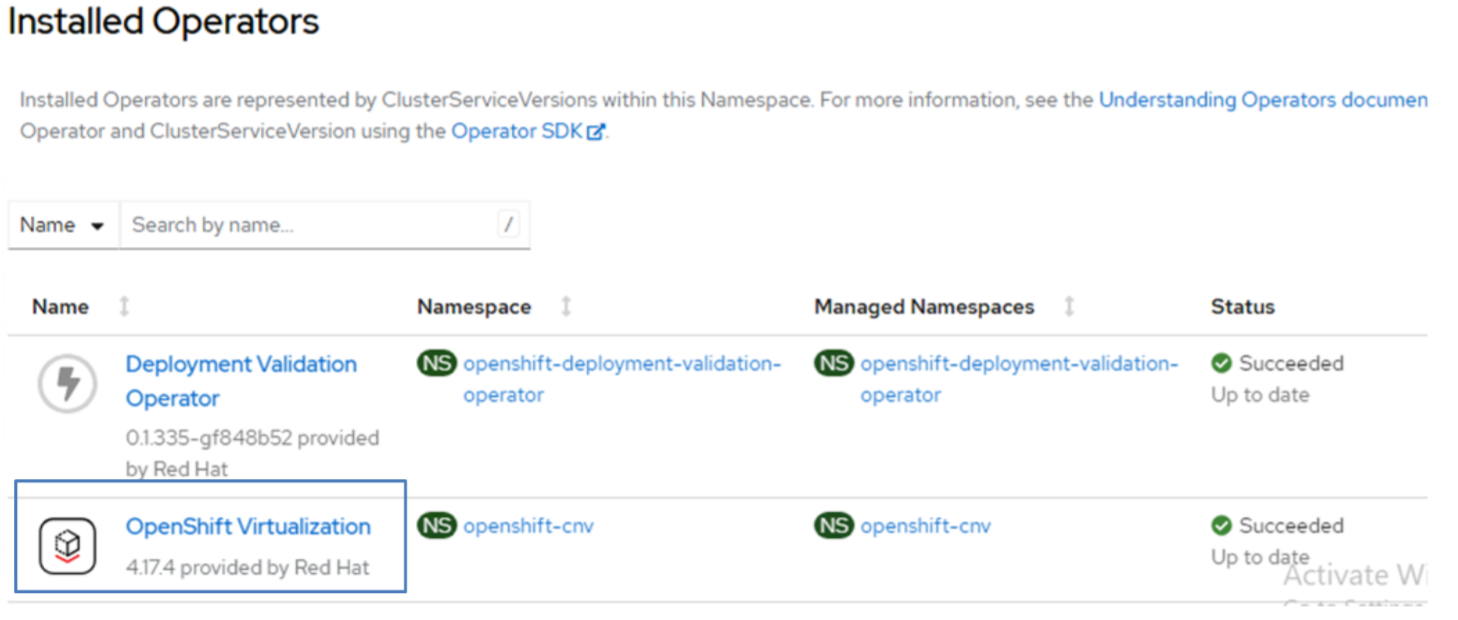
Figure 2
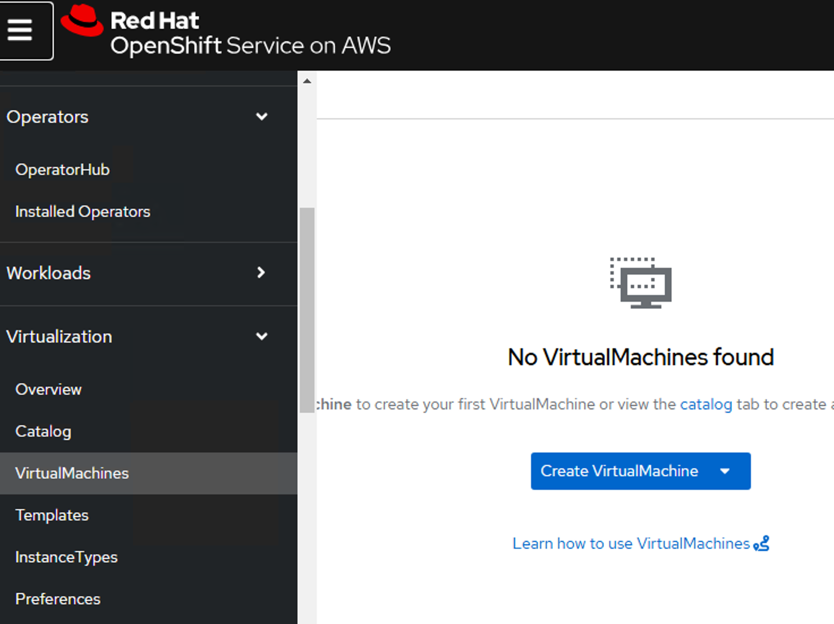
Figure 3: The screen shot above shows that currently there are no VMs running on the cluster.
Deploy a VM using iSCSI storage class
- Click on Create VirtualMachine (see Figure X) and select From template.
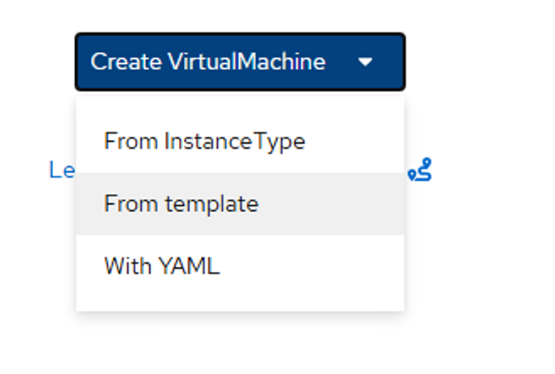
Figure 4 - Select Fedora VM.
Note: You can choose any OS that has a source available.
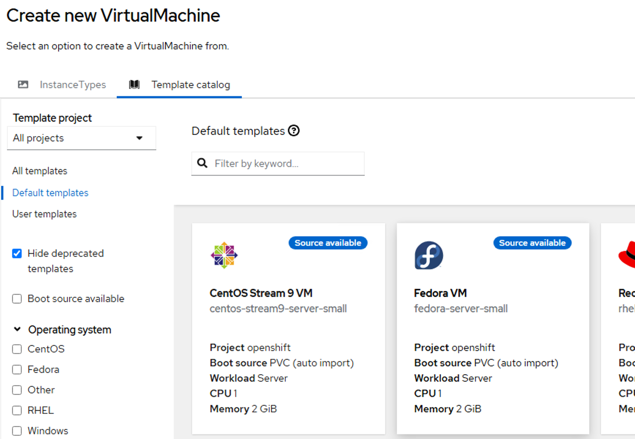
Figure 5
Customize the VM
Customize the VM to provide the storage class for the boot disk and create additional disks with the selected storage class.
- Click on Customize VirtualMachine.
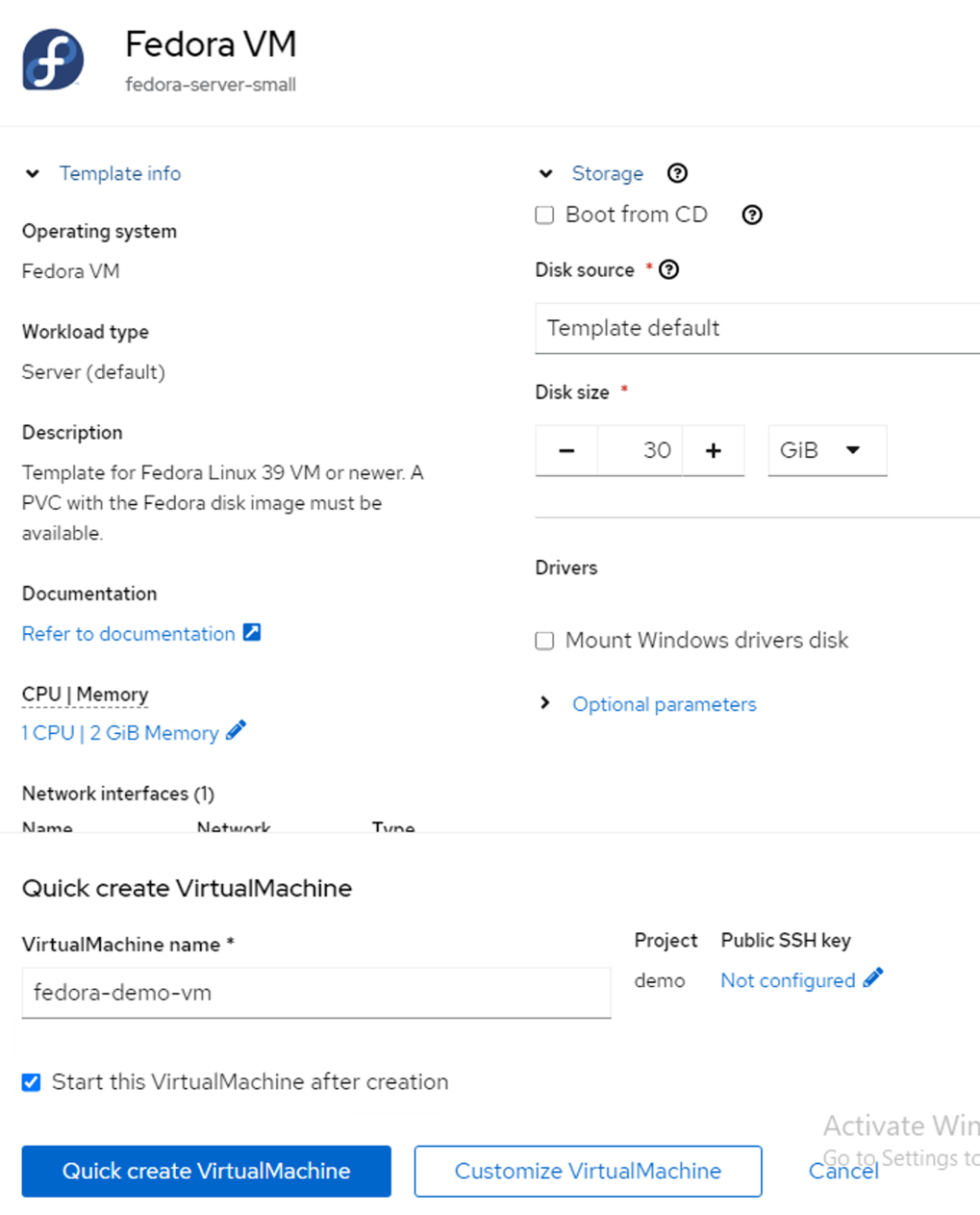
Figure 6
- Click on the Disks tab and click on Edit for the root disk
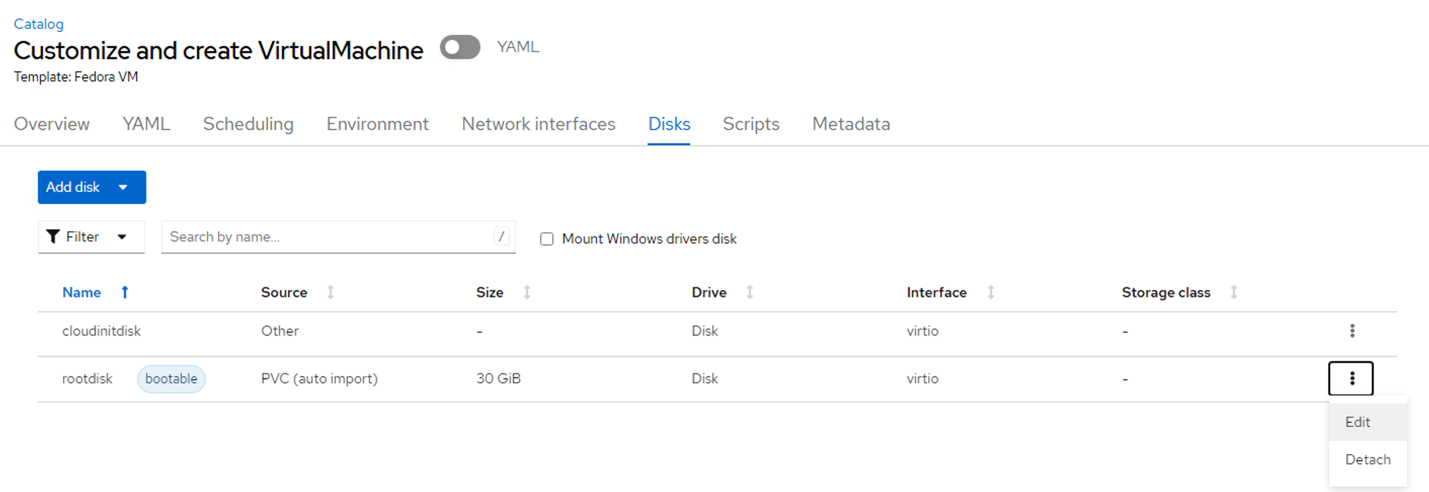
Figure 7 - Ensure you have selected sc-fsx-san for storage class.
- Select Shared Access (RWX) for Access Mode and select Block for Volume Mode. Trident Supports RWX Access mode for iSCSI storage in Volume Mode Block. This setting is a requirement for the PVC of the disks so that you can perform live migration of VMs. Live migration is migration of a VM from one worker node to another for which RWX access mode is required and Trident supports it for iSCSI in Block Volume Mode.
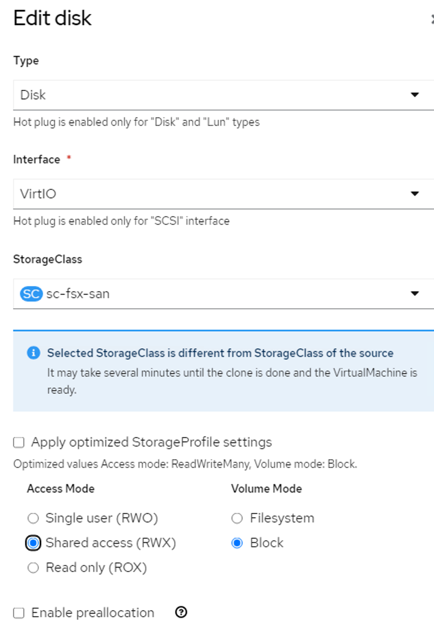
Figure 8- Note: If you check the Apply optimized StorageProfile Settings, then it automatically chooses RWX and Volume mode Block. If sc-fsx-san was set as the default storage in the cluster, then this storage class will automatically be picked.
- Click Add disk and select empty disk (since this is just an example) and ensure that sc-fsx-san disk is chosen (Figure 9). Make sure the optimized StorageProfile setting is checked. Click Save and then click Create VirtualMachine (Figure 10). The VM comes to a running state (Figure 11).
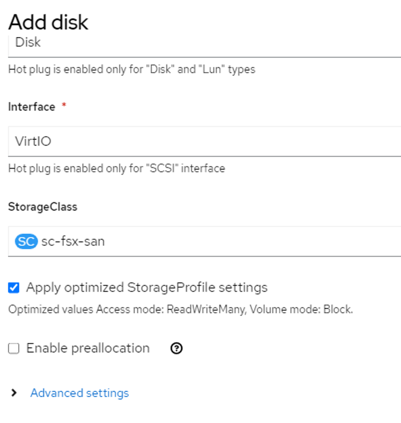
Figure 9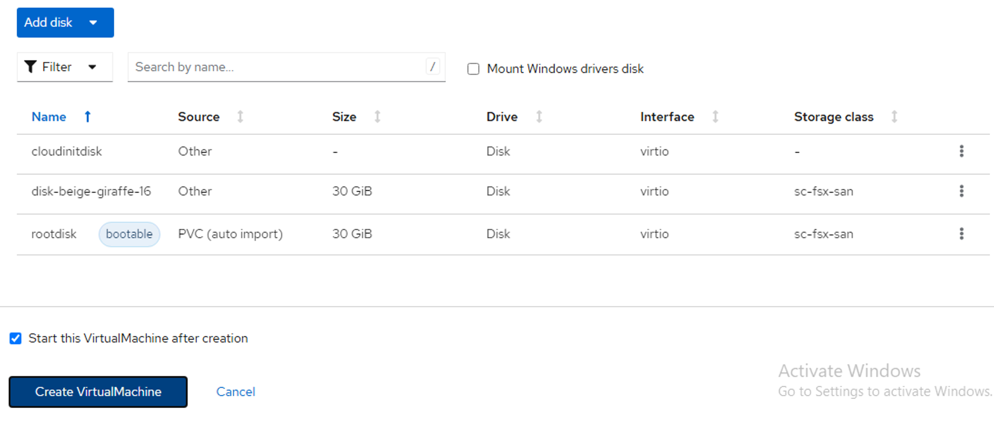
Figure 10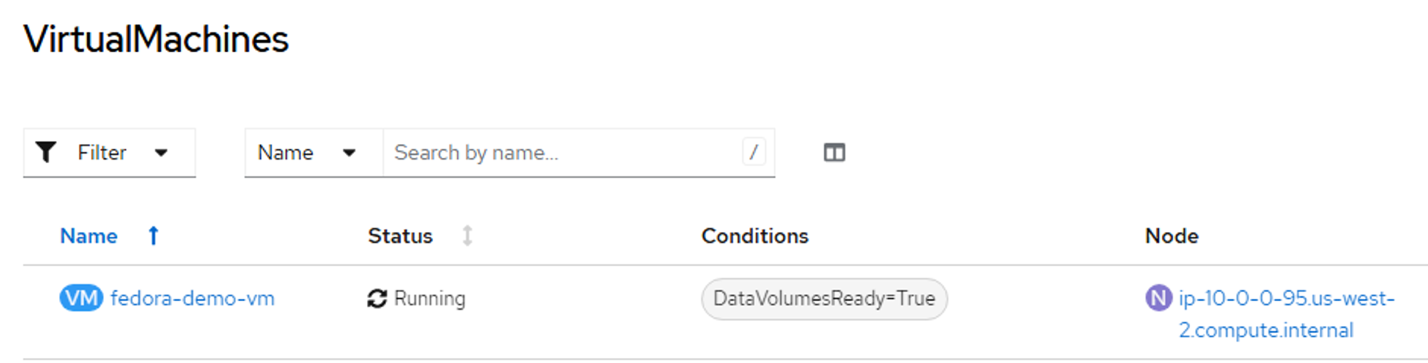
Figure 11 - Check the VM pods, PVCs. Verify that PVCs are created using iSCSI storage class and RWX Access modes.
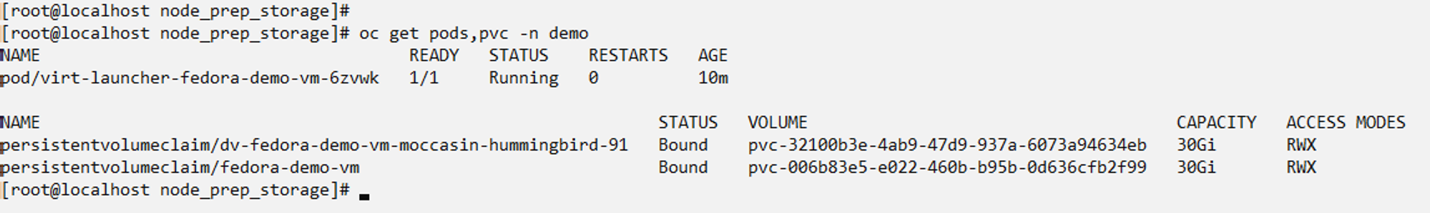
Figure 12 - Verify that a LUN is created in each volume corresponding to the disk PVCs by logging into the FSxN CLI.
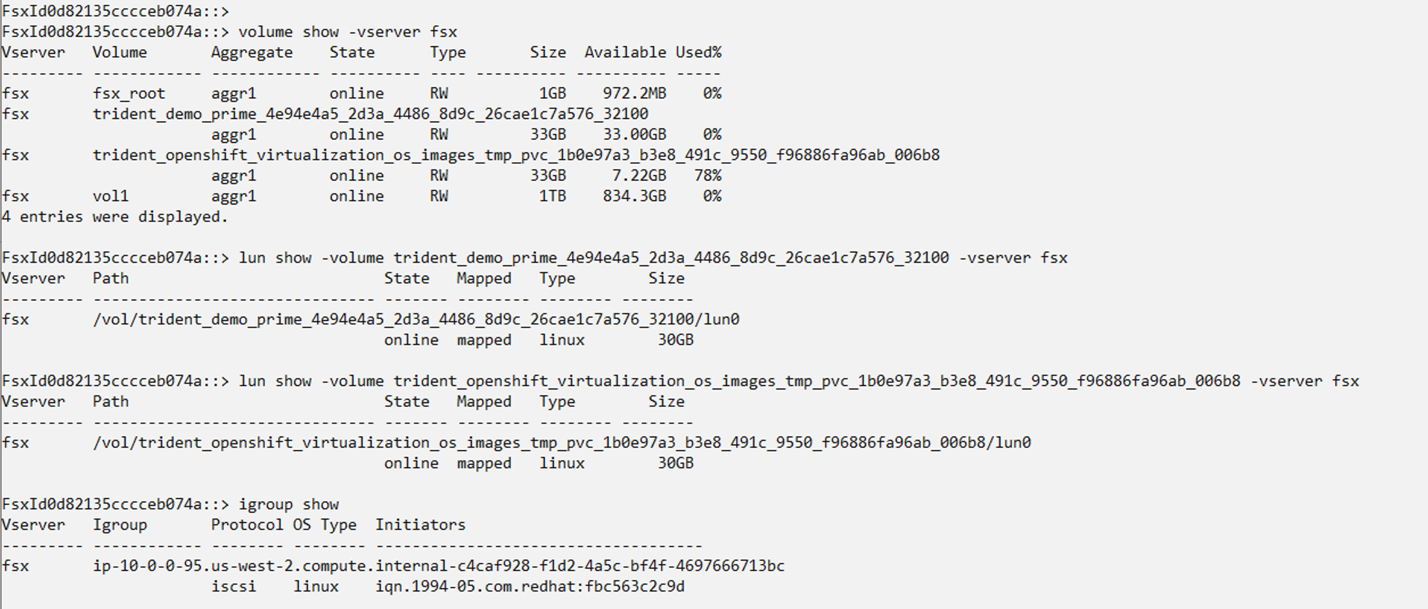
Figure 13
You have now successfully deployed and customized VMs using iSCSI storage class with Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization!
