Installation and key functionalities
While the process of installing Red Hat® Ansible® Automation Platform is relatively straightforward, it’s important to understand what it’s made of in order to navigate it properly. Here we’ll look at key terms that are unique to Ansible, what they mean, and what to do with them.
What will you learn?
- The basic key components of Ansible Automation
What do you need before starting?
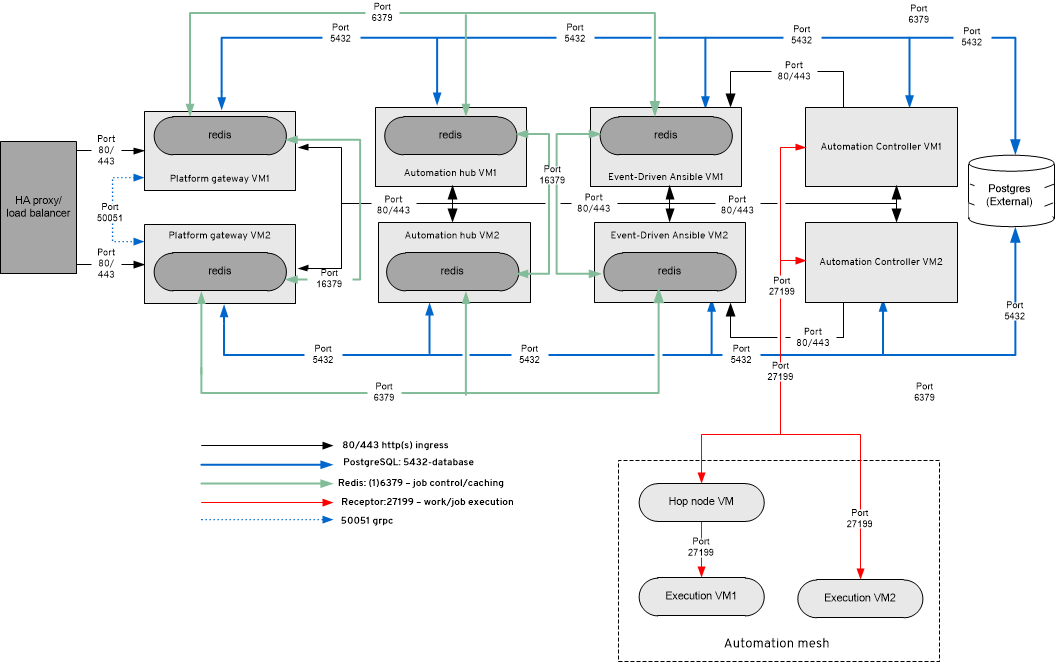
Installation options
Installing Ansible is a quick process. However, it can be deployed in a number of environments, so it’s important to take stock of how exactly you want it to work for your infrastructure. For the purposes of this learning path, we will be exploring cloud deployment options.
Cloud-based deployment options
- Public cloud: One Ansible deployment option is through any public cloud, including Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. This is useful if your infrastructure or organization already has an existing provider that they wish to continue using.
- Managed deployment: This allows Red Hat and you to share responsibility in managing Ansible Automation Platform.
- Self-managed deployment: A more flexible option for users that want to customize and manage their environment directly with no additional Red Hat input.
Once you decide on a deployment option, there are several installation guides to get it set up within your own unique environment.
After you have your installation completed, it’s best to dig into the components of it before fully jumping into using the platform.
Key functionalities of Ansible
Ansible Automation Platform includes several key items that you’ll interact with while creating, managing, and scaling your automation use:
- Ansible automation content: This is a central repository to discover, download, and manage Ansible Content Collections, as well as validated content.
- Private automation hub: Manage, share, and curate your organization’s automation content and control access to certified and validated Red Hat and partner-created content with a repository that can sit behind your firewall or on disconnected systems.
- Automation execution (automation controller): This control plane is used to deploy, initiate, delegate, and audit automation for Ansible Automation Platform. This is one of the more basic and used functionalities that most users learn.
- Automation mesh: Mesh is a means of scaling your automation across diverse network topologies, platforms, and teams with an overlay network that simplifies the distribution of automation tasks using existing connectivity.
- Automation decisions (event-driven Ansible): This particular functionality of Ansible focuses on automatic responses to changing IT conditions. Automation decisions have the capabilities of pivoting in real time when things don’t go as planned. See how in this hands-on lab.
Each of these components works together within the overall Ansible Automation Platform architecture.