Deploying and Managing Virtual Machines on ROSA with OpenShift GitOps
This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
One of the great things about OpenShift Virtualization is that it brings new capabilities to run virtual machines alongside your containers AND using DevOps processes to manage them.
This tutorial will show how to configure OpenShift GitOps ( based on ArgoCD ) to deploy and managed virtual machines.
Pre-requisites
- A ROSA Cluster with OpenShift Virtualization (see Deploying OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA ) If you follow the guide above, you can skip the Create a Virtual Machine section as we will be using OpenShift GitOps to deploy the cluster.
Note: If you get a 404 error when you depoy “HyperConverged”, make sure your metal nodes are ready and have enough capacity.
- The
gitbinary installed on your machine. You can download it from the git website .
Prepare the Environment
Retrieve the source code to deploy VMs with OpenShift GitOps
git clone https://github.com/rh-mobb/rosa-virt-gitops cd rosa-virt-gitops
Install the OpenShift GitOps Operator
cat << EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: openshift-gitops-operator
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1
kind: OperatorGroup
metadata:
name: openshift-gitops-operator
namespace: openshift-gitops-operator
spec:
upgradeStrategy: Default
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: openshift-gitops-operator
namespace: openshift-gitops-operator
spec:
source: redhat-operators
installPlanApproval: Automatic
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
name: openshift-gitops-operator
channel: latest
EOF
Configure OpenShift GitOps
Give OpenShift GitOps Permissions
The following command will give the OpenShift GitOps service account cluster admin privileges so it can deploy VMs to any namespace.
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin system:serviceaccount:openshift-gitops:openshift-gitops-argocd-application-controllerCreate an OpenShift GitOps Application Set
For demonstrations purposes, we will deploy two VMs, one for Dev and one for Production. Usually, these VMs would be deployed to different clusters but the sake a simplicity, we will deploy these VMs to different namespaces.
oc apply -n openshift-gitops -f applicationsets/vm/applicationset-vm.yamlVerify the applications ( VMs ) were created in OpenShift GitOps.
Retrieve and open the OpenShift GitOps URL.
oc get route openshift-gitops-server -n openshift-gitops -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}{"\n"}'expected output
openshift-gitops-server-openshift-gitops.apps.rosa.kevcolli-hcp1.dp4i.p3.openshiftapps.comOpen the url in a browser and notice there are two ArgoCD applications that were created.
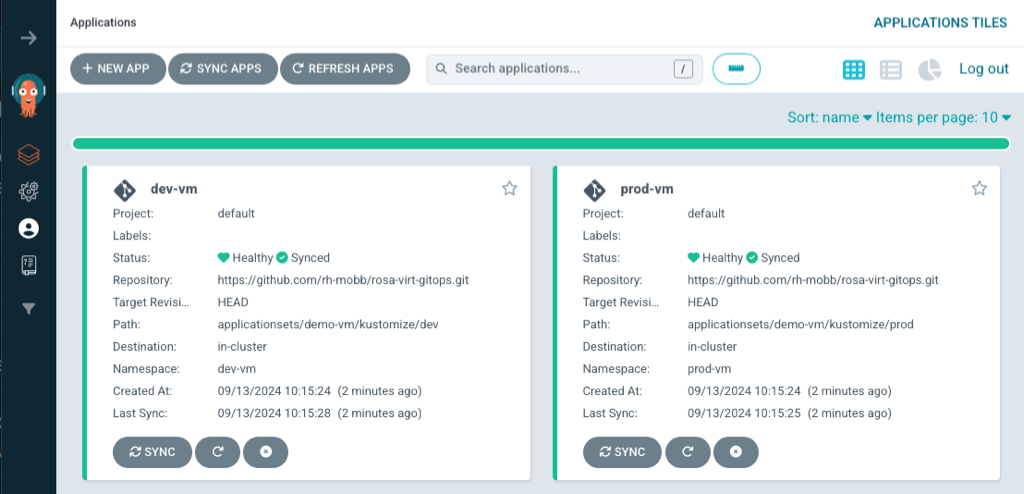
Notice there is one application for dev and one for prod.
Click into one of the applications, and see that everything is synced and all the resources that were created.
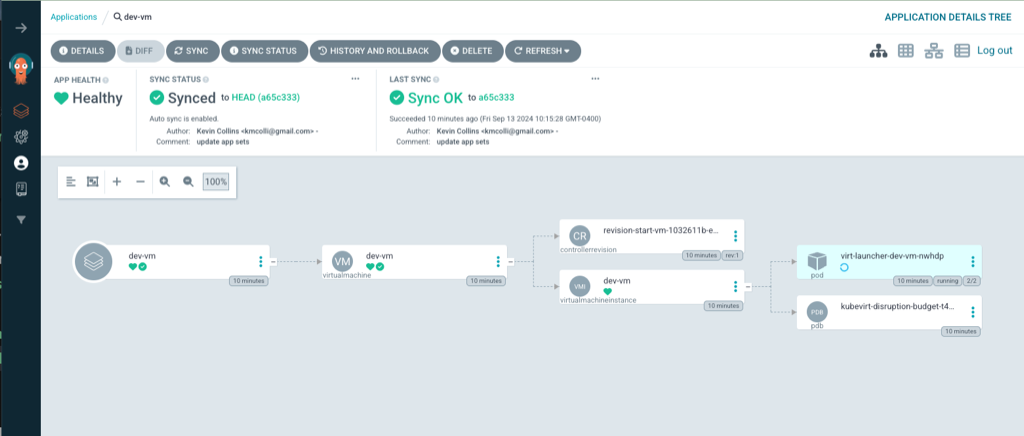
Next, let’s view the virtual machines that were created.
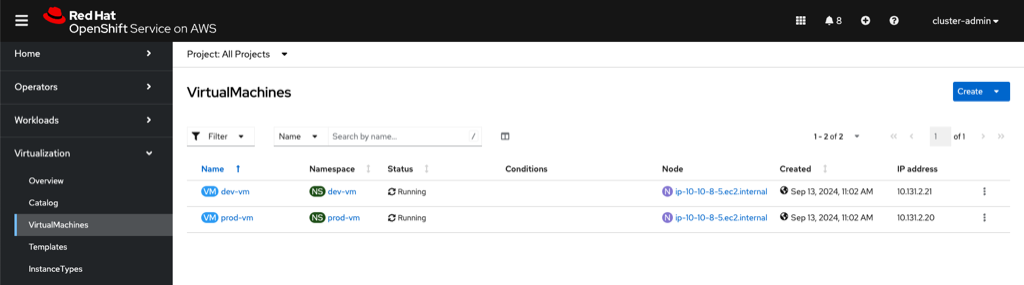
In the OpenShift console, from the menu click on Virtualization and the Virtual Machines. Make sure All Projects is selected.
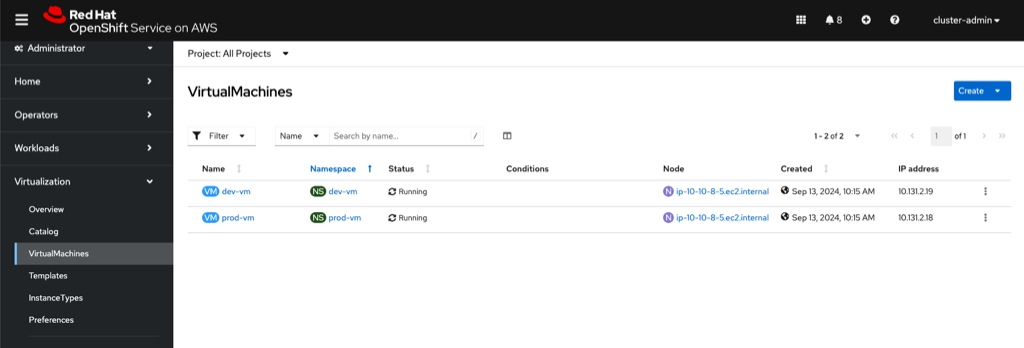
Notice that there is a dev-vm which is in the dev-vm namespace and a prod-vm in the prod-vm namespace.
Manually change a VM
One of the great benefits of OpenShift GitOps is that it will keep the state of the resources that you specified.
If you look at the VirtualMachine definition at VirtualMachine , notice that the Virtual Machine is specified as it should be running.
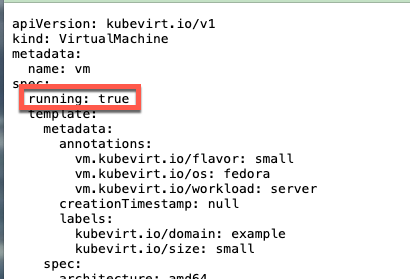
When the ArogCD ApplicationSet was applied, self healing was set to true.
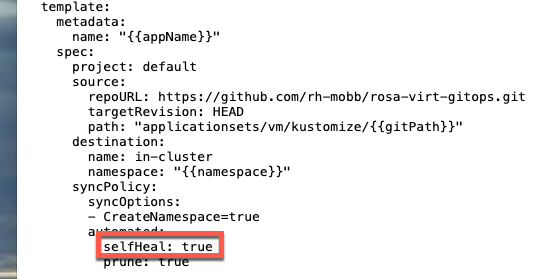
What this means is if we do something like stop the VM, Argo will restart it automatically. Let’s test it out.
Make sure to have the ArgoCD UI up and ready in a new tab, the change happens very fast.
From the list of VMs, click on Stop next to the Dev VM. Once you click stop, switch over to the ArgoCD tab.
Switching over the ArgoCD UI, noticed the App Healh shows “Progressing” and the dev-vm is being started.
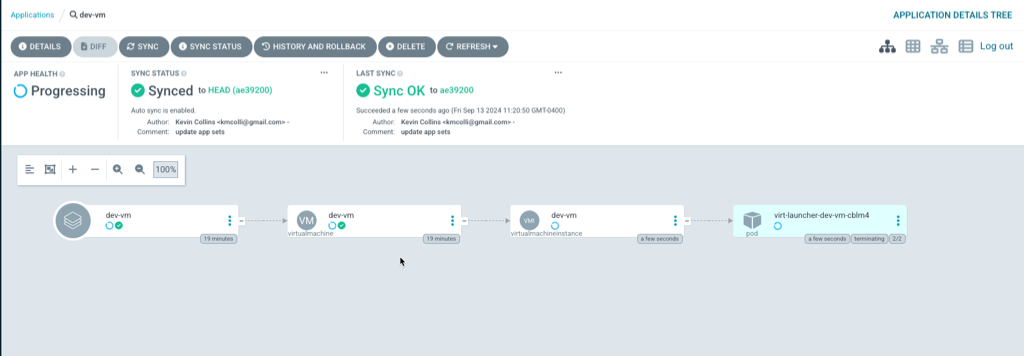
After a few seconds, the Application shows health again and the vm is running.
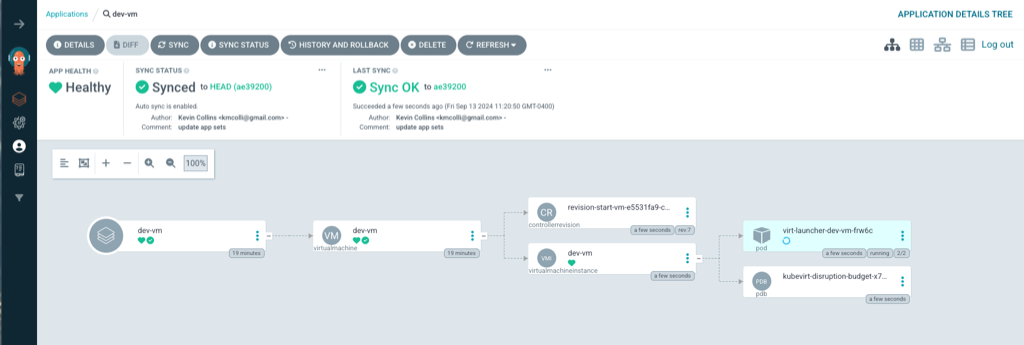
Navigating back to the list of VMs in OpenShift, both VMs are running.
That is one of the superpowers of OpenShift GitOps in that it keeps you applications in sync as there were specified in Git, elimiating application drift.
Make changes to the virtual machines through git.
Start by deleting the ArgoCD application set, VMs that we created using this tutorials github repo.
oc delete ApplicationSet vms -n openshift-gitops
Next, fork the tutorial github
repo
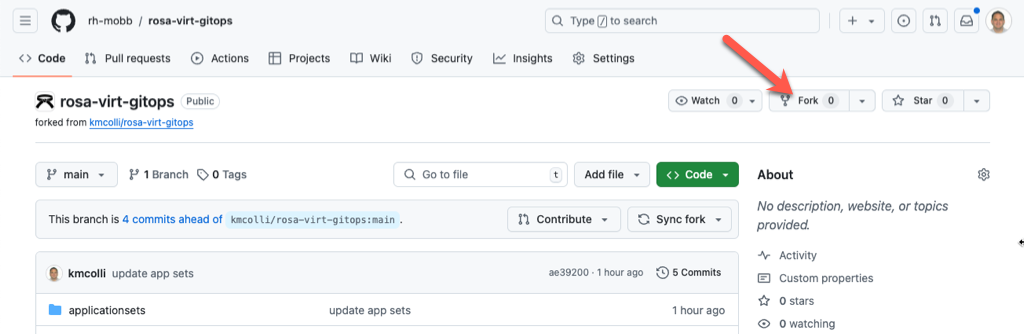
Export an environment variable with your GitHub username
export GIT_USERNAME=<YOUR GITHUB USERNAME>
Clone the repo in YOUR github account locally:
git clone https://github.com/$GIT_USERNAME/rosa-virt-gitops
cd rosa-virt-gitops
Open the applicationset-vm.yaml file located at applicationsets/vm/applicationset-vm.yaml and change the repoURL to your repo. Ex.
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/<GIT_USERNAME>/rosa-virt-gitops.git
Save the file, and push to git.
git commit -am "update applicationset-vm repo usrl"
git push
Create an ApplicationSet and VMs using your github repo
oc apply -n openshift-gitops -f applicationsets/vm/applicationset-vm.yaml
The result should look exactly like you saw previously with 2 ArgoCD apps and 2 VMs one for dev and one more prod.
Argo UI

List of VMs.

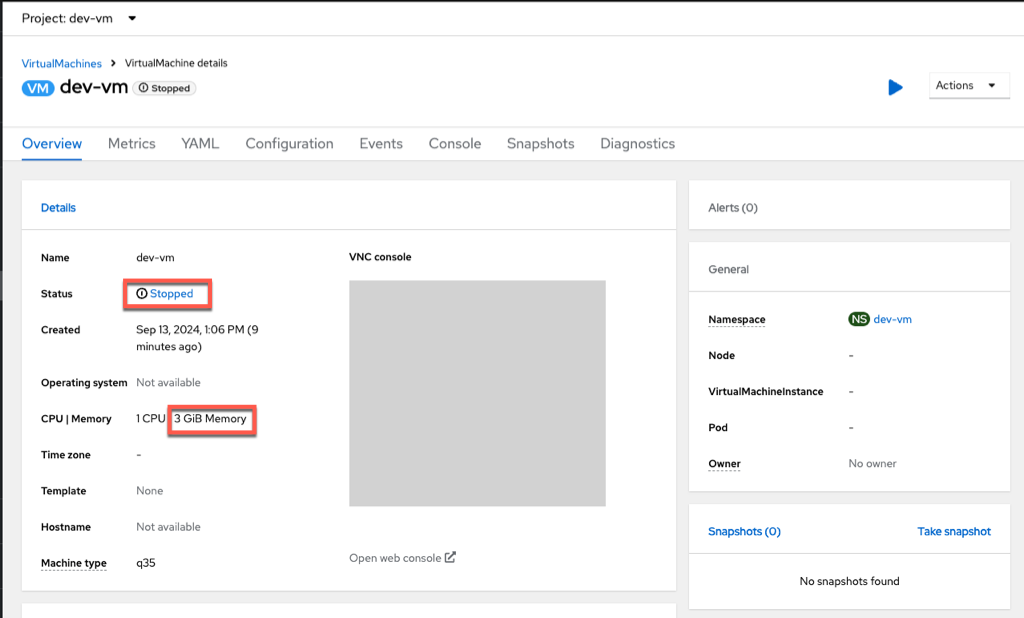
Now, let’s make a change to VirtualMachine definition in having the Virtual Machine state being stopped and increasing the amount of memory requested.
Open the dev kustomization file located at /applicationsets/vm/kustomize/dev/kustomization.yaml
Change the patch section with the following:
- patch: |
- op: replace
path: /spec/running
value: false
- op: replace
path: /spec/template/spec/domain/memory/guest
value: 3Gi
- op: replace
path: /spec/template/spec/volumes/1/cloudInitNoCloud/userData
value: |-
#cloud-config
user: fedora
password: fedora123
chpasswd: { expire: False }
Save the file, and push to git.
git commit -am "stopping the VM and increasing memory"
git push
Next, let’s switch back over to ArgoCD and sync our changes. From the dev-vm application in ArgoCD, slick on Sync.
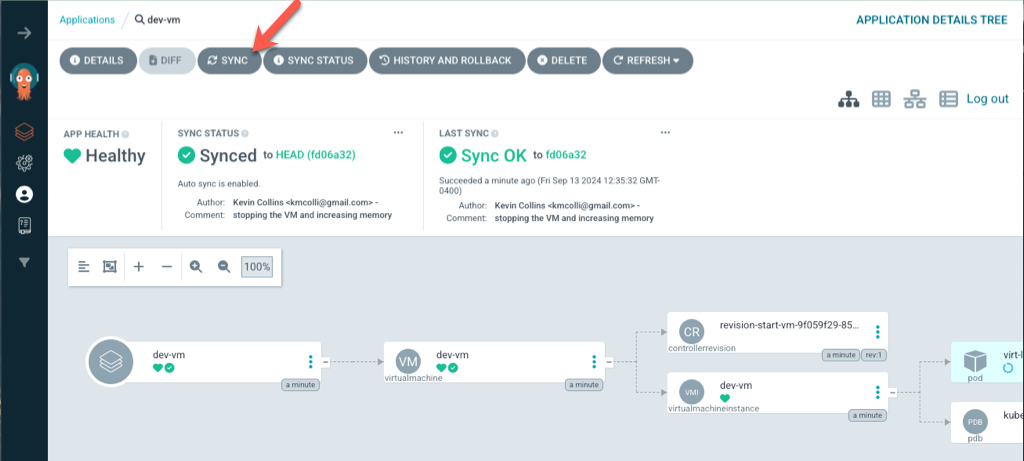
on the next popup screen, keep the default and click synchronize
This will stop the dev vm and increase the memory to 3GB. To verify, click into the dev-vm and see the results.