Deploying OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA (GUI)
This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
OpenShift Virtualization is a feature of OpenShift that allows you to run virtual machines alongside your containers. This is useful for running legacy applications that can’t be containerized, or for running applications that require special hardware or software that isn’t available in a container.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to deploy OpenShift Virtualization on Red Hat OpenShift on AWS (ROSA) using the OpenShift Console. I’ll show you how to deploy the OpenShift Virtualization operator, and create a virtual machine all from inside the Red Hat Cluster Manager and OpenShift Console
It’s important to keep in mind that this tutorial is designed to show you the quickest way to get started with OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA. It’s not designed to be a production-ready deployment. If you’re planning to deploy OpenShift Virtualization in a production environment, you should follow the official documentation and best practices.
If you don’t want to deploy the resources yourself, you can watch the video below to see how it’s done.
Pre-requisites
You will need a A ROSA Cluster (see Deploying ROSA HCP with Terraform if you need help creating one).
Browse to the OpenShift Cluster Manager and select your cluster, then click on the “Machine Pools” tab.
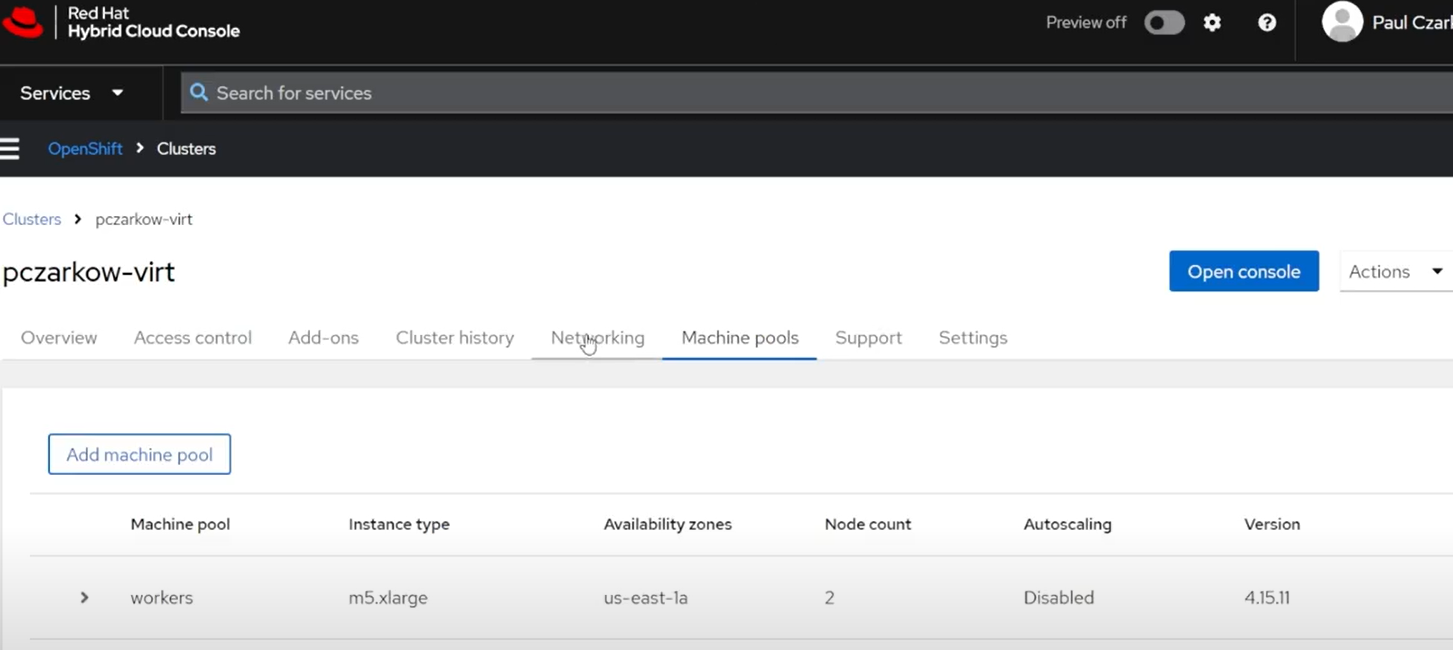
Click on the “Add Machine Pool” button, give it a name, and select a Bare Metal instance type such as
m5zn.metal, set replicas to1and clickAdd machine pool.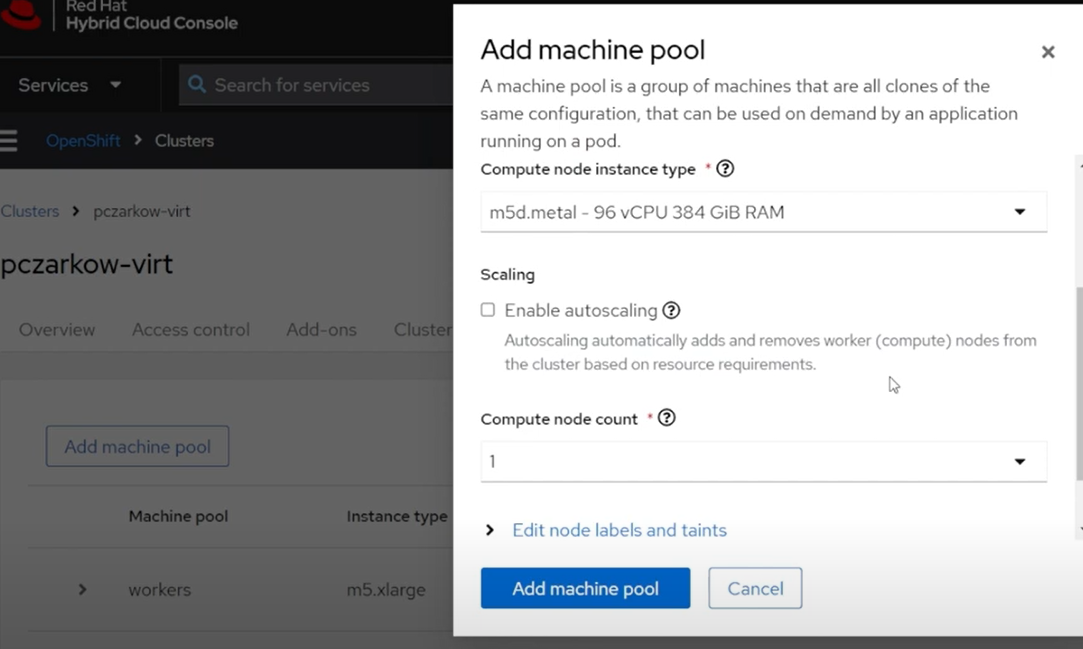
When that’s done, click on the
Open Consolebutton to open the OpenShift Console, then go to the Operators -> OperatorHub page and search forVirtualization.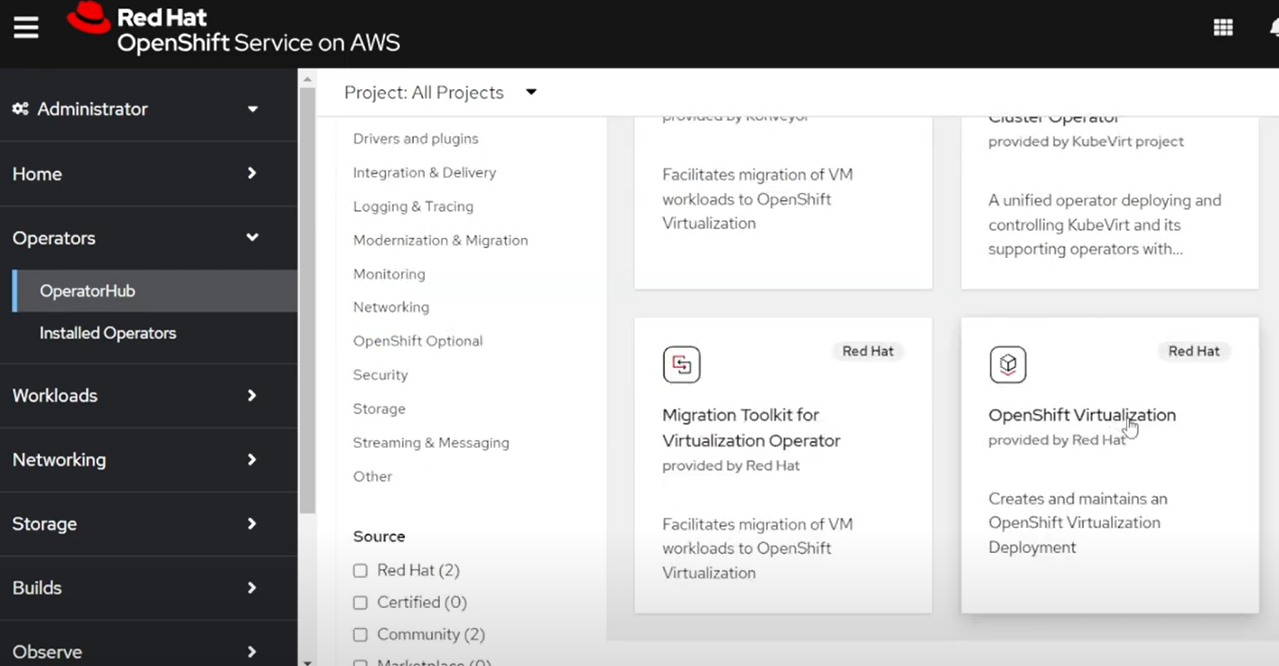
Accept all the defaults and click the blue “Install” button. Once installed it should prompt you to Create a
HyperConvergedinstance, click the blueCreate HyperConvergedbutton. Once again accept all of the defaults.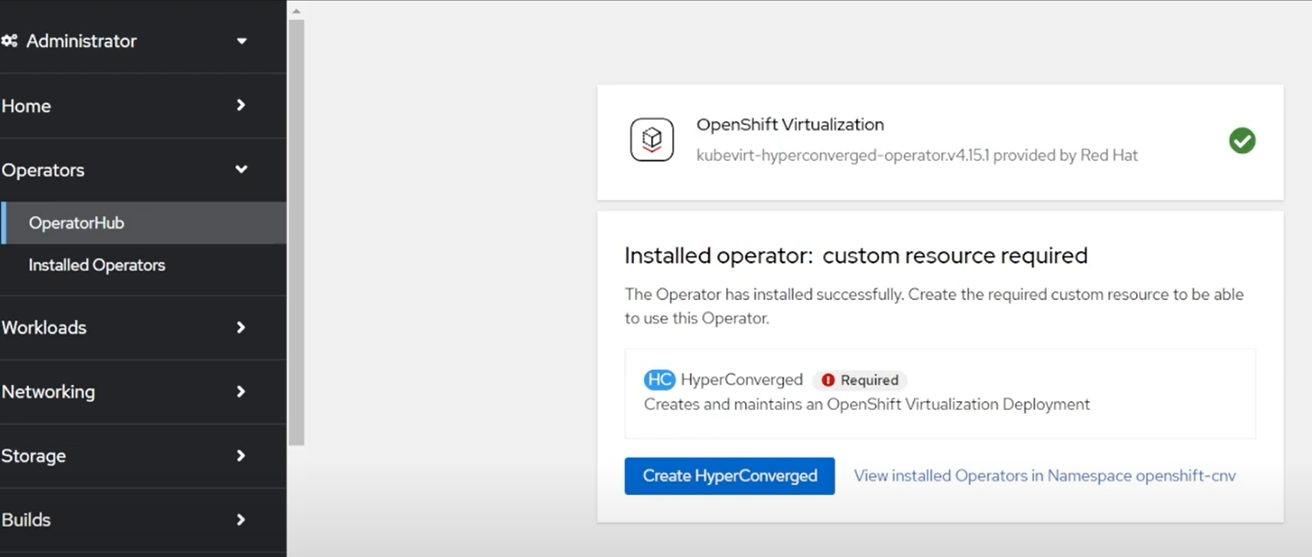
Once deployed it should notify you that you should refresh your browser, after which there will be a new
Virtualizationmenu item in the left-hand navigation, click on that and thenCatalog->Template catalog.Note: Make sure you’re in the
defaultproject (or create a new one)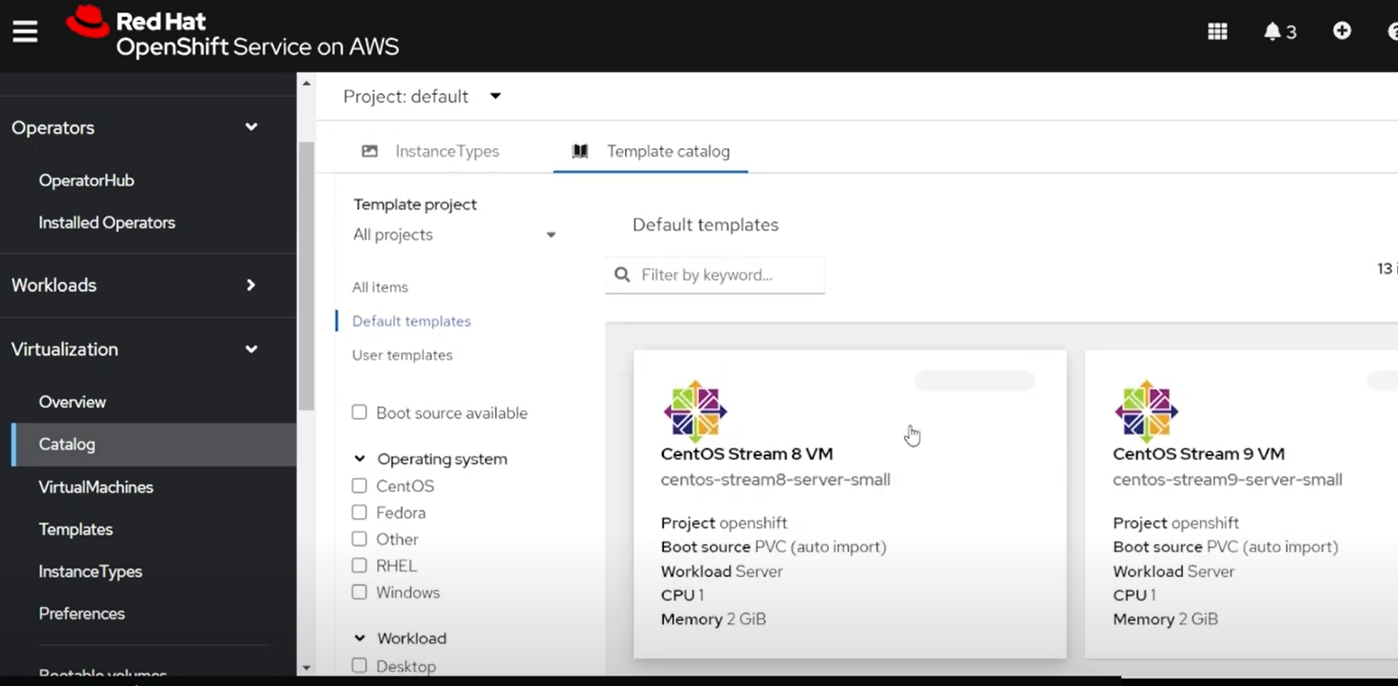
Pick your preferred OS, in this case, we’ll use
CentOS Stream 8 VM, click on that and then clickCustomize VirtualMachine.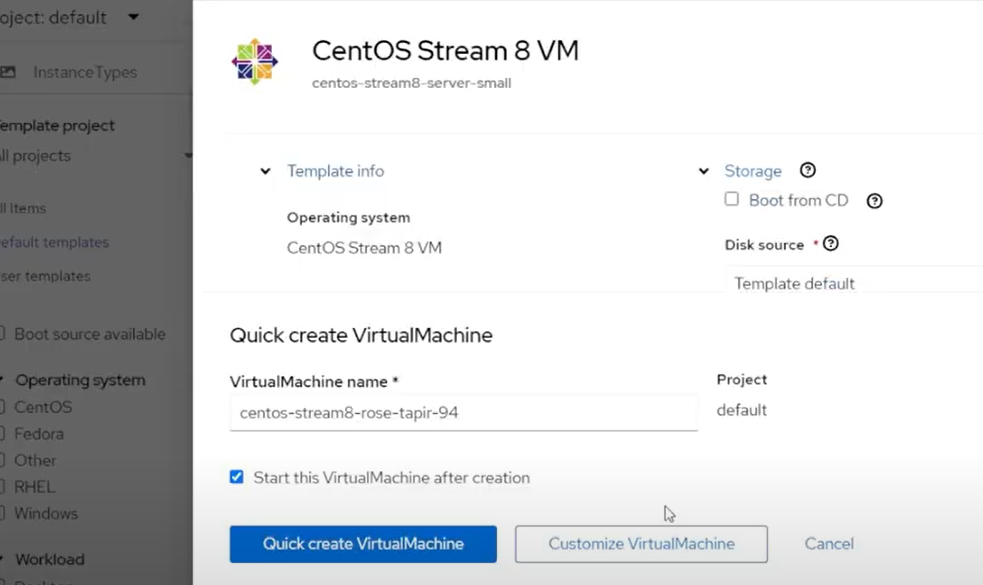
Click on the
Scriptstab, and click theEditbutton next to thePublic SSH Keytitle. Click “Add new” and paste in your public SSH key, check theAutomatically apply this key to any new Virtual Machine you create in this projectthen clickSave.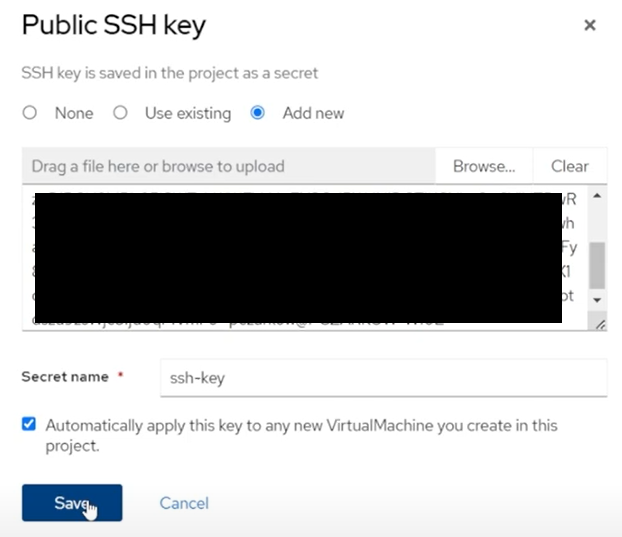
Click
Create VirtualMachine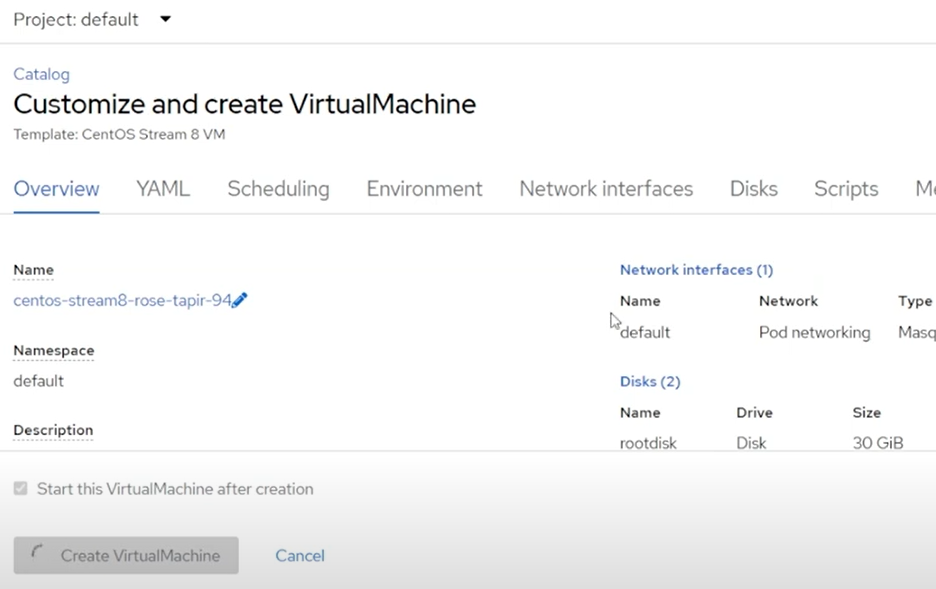
After a while the VM will be running and you’ll see a preview of the VNC console.
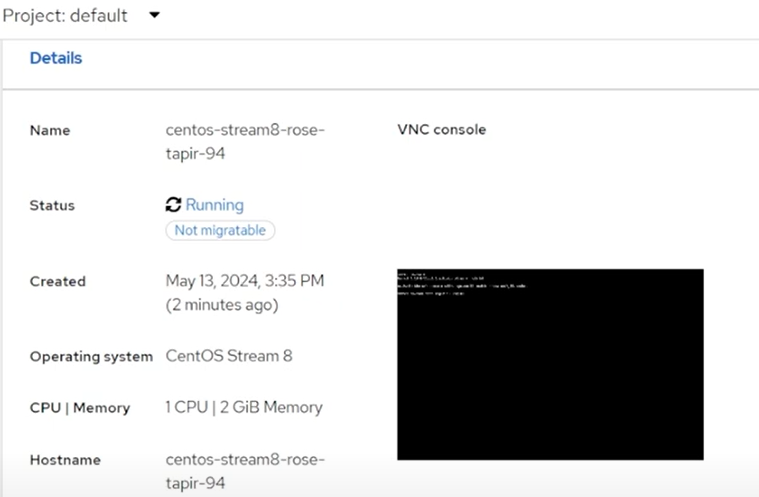
From here you can click
Open web consoleto get an interactive VNC console, or you can SSH into the VM using thevirtctlcommand.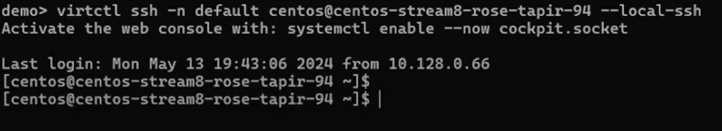
Congratulations! You now have a virtual machine running on OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA!
