Deploying OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA (CLI)
This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
OpenShift Virtualization is a feature of OpenShift that allows you to run virtual machines alongside your containers. This is useful for running legacy applications that can’t be containerized, or for running applications that require special hardware or software that isn’t available in a container.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to deploy OpenShift Virtualization on Red Hat OpenShift on AWS (ROSA). I’ll show you how to create a ROSA cluster, deploy the OpenShift Virtualization operator, and create a virtual machine.
It’s important to keep in mind that this tutorial is designed to show you the quickest way to get started with OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA. It’s not designed to be a production-ready deployment. If you’re planning to deploy OpenShift Virtualization in a production environment, you should follow the official documentation and best practices.
If you don’t want to deploy the resources yourself, you can watch the video below to see how it’s done.
Pre-requisites
You will need a A ROSA Cluster (see Deploying ROSA HCP with Terraform if you need help creating one).
Set the cluster name as an environment variable (in the example we re-use the variable from the Terraform guide). ort METAL_AZ=$(terraform output -json private_subnet_azs | jq -r ‘.[0]’)
Create a bare metal machine pool
Note bare metal machines are not cheap, so be warned!
Deploy the OpenShift Virtualization Operator
Deploy the OpenShift Virtualization Operator
If you want to see the progress of the operator you can log into the OpenShift Console (hint run
oc whoami --show-consoleto get the URL)
Create an OpenShift Virtualization operand
Note: this is all defaults, so will not support a lot of the more advanced features you might want such as live migration.
New “Virtualization” Section in the OpenShift Console
Once the operator is installed you should see a new “Virtualization” section in the OpenShift Console (you may be prompted to refresh the page)
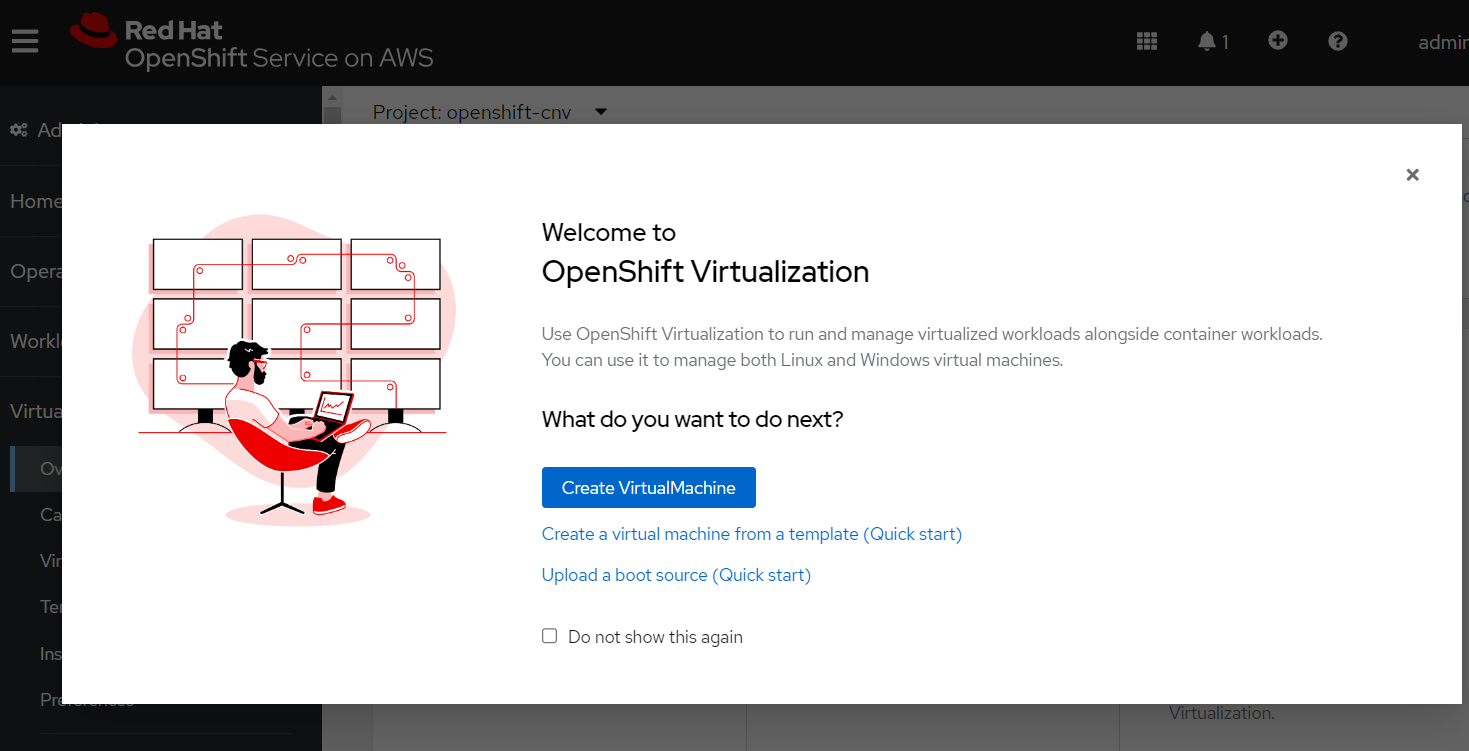
Close the popup window and click the “Download virtctl” button to download the
virtctlbinary.
Create a Virtual Machine
Create a project and a secret containing your public SSH key
Create a VM
Start the VM
Watch for the VM to be ready
Every 2.0s: oc get vm NAME AGE STATUS READY example-vm 3m16s Running False
SSH into the VM
Congratulations! You now have a virtual machine running on OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA!
Cleanup
Delete the VM
Delete the ROSA Cluster
